5-Axis CNC Machining: Complete Guide to Advanced Manufacturing Technology
Discover how 5-axis CNC machining revolutionizes precision manufacturing. Learn about the technological advantages, applications, and future trends of five-axis machining compared to 3-axis and 4-axis systems. This comprehensive guide covers everything from micron-level precision to intelligent automation in modern CNC technology.
In the evolution of CNC machining technology, the progression from 3-axis to 4-axis and finally to 5-axis CNC machining represents far more than a simple addition of rotational axes. This advancement marks a fundamental transformation in precision manufacturing, redefining the boundaries of what’s possible in terms of accuracy, efficiency, and complex part production. This guide explores the core advantages of five-axis machining, the development of 5-axis CNC systems, key technologies, and future trends in intelligent manufacturing.
Understanding the Evolution: From 3-Axis to 5-Axis CNC Machining
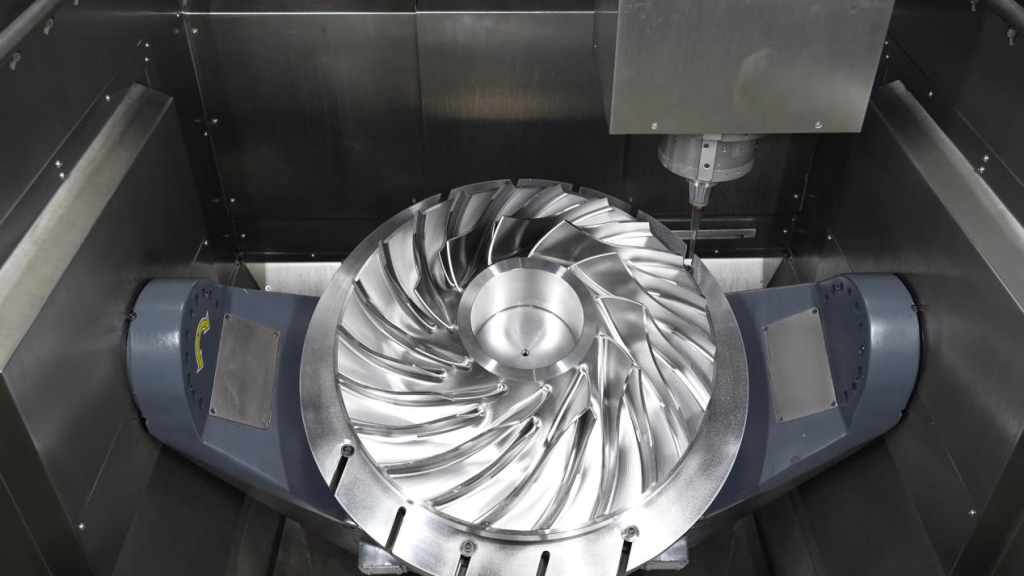
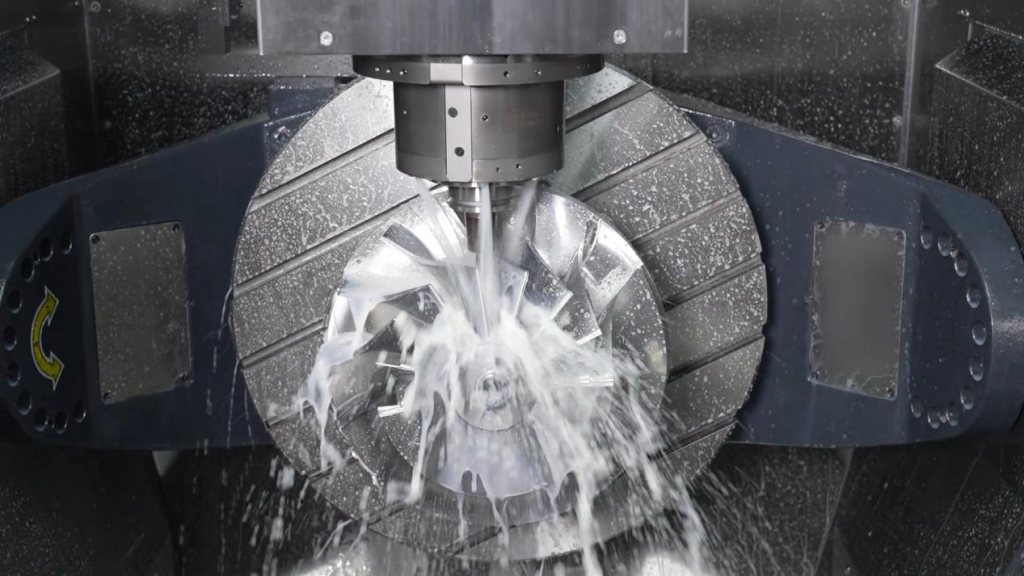
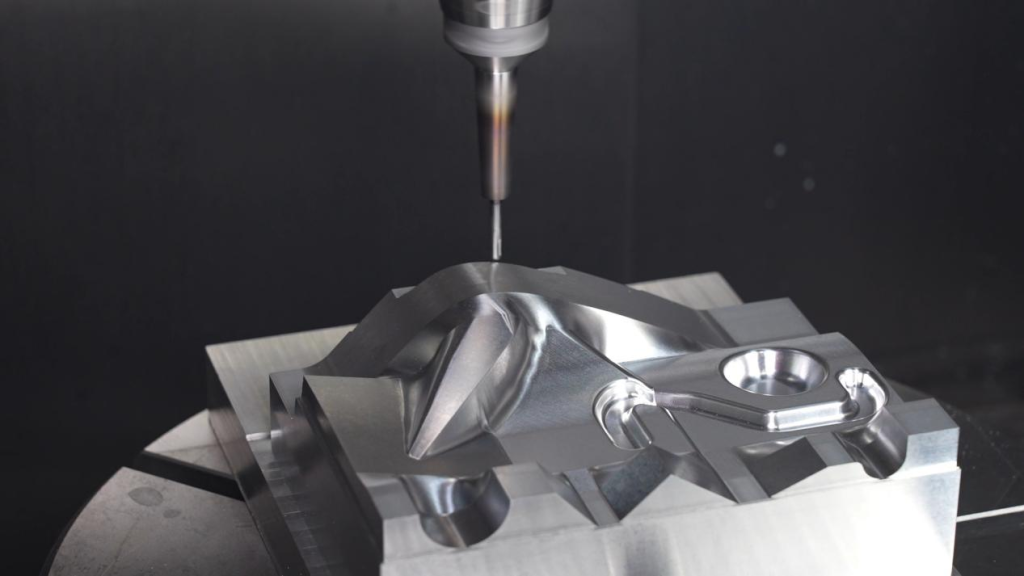



3-Axis CNC Machining: The Foundation of Precision Manufacturing
Traditional 3-axis CNC machinesoperate using X, Y, and Z linear axes for coordinated cutting. The cutting tool moves along these fixed directions while the workpiece remains stationary, similar to a paintbrush operating on a two-dimensional plane. This CNC machining method offers several advantages:
• Simple structure and lower equipment costs
• Easy operation and programming
• Ideal for planar parts and simple curved surfaces
• Achieves accuracy up to 0.01mm
• Perfect for applications like gear manufacturing
However, 3-axis machining faces limitations. The extended cutting tool length required for this configuration creates vibration issues, necessitating secondary processing for surface finish. Complex parts require multiple clamping operations, each introducing potential positioning errors that compound accuracy issues.
4-Axis CNC Machining: Adding Rotational Capability
The introduction of 4-axis machining adds a rotary axis (typically A or B axis) to the standard three linear axes. This CNC technology advancement enables:
• Single-setup multi-face machining capabilities
• Reduced positioning errors through fewer setups
• 30% efficiency improvement over 3-axis systems
• Enhanced capability for spiral grooves and turbine blade manufacturing
While 4-axis CNC machining represents a significant step forward, single-axis rotation cannot achieve complete spatial coverage. Complex geometries like impeller backs remain challenging, making this a transitional technology between 3-axis and 5-axis machining
5-Axis CNC Machining: Complete Spatial Freedom
5-axis machining technology integrates two rotary axes (commonly A/C or B/C configurations) with the standard X, Y, and Z linear axes, achieving true five degrees of freedom. This advanced CNC machining capability delivers:
• Complete part machining in a single setup
• Smooth processing of complex curved surfaces
• Elimination of tool interference issues
• Reduced tool wear and extended tool life
• Integrated manufacturing of highly complex components
Three Core Advantages of 5-Axis CNC Machining
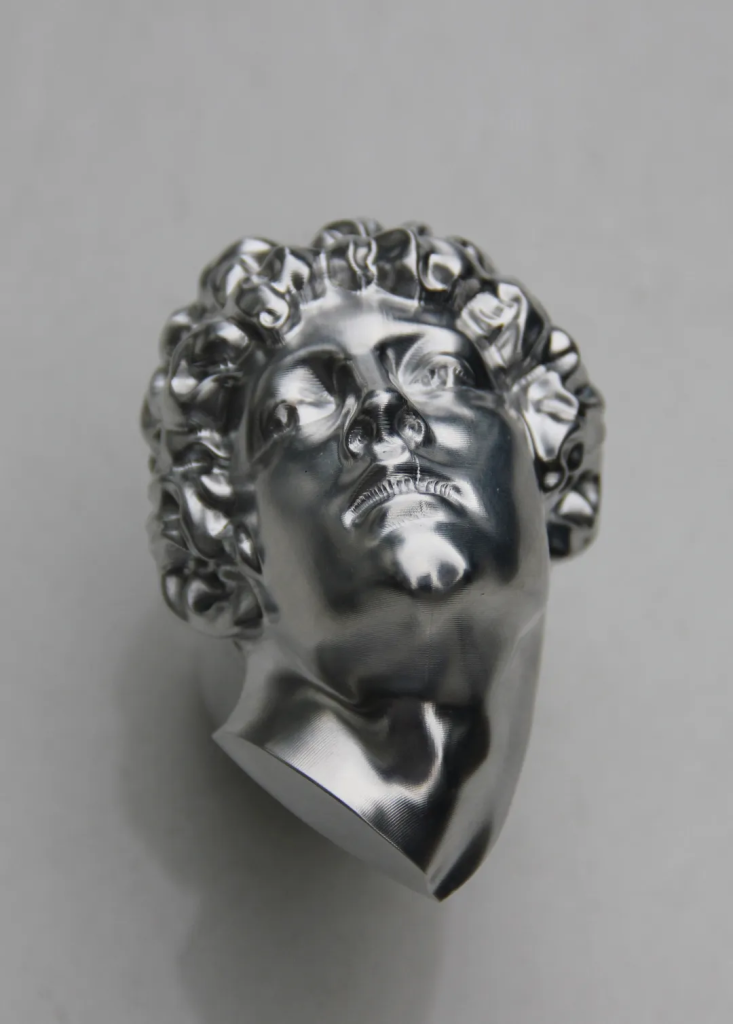
1. Micron-Level Precision Through Single-Setup Manufacturing
The most significant advantage of 5-axis CNC machiningis its ability to complete all machining operations in one setup. By eliminating repeated workpiece repositioning, this precision machining technology fundamentally prevents cumulative positioning errors.
Key precision benefits:
• Positioning accuracy stable within 0.005mm (micron-level precision)
• Aero-engine blade manufacturing: 99% pass rate (vs. 85% with 3-axis)
• Medical implants: micron-level biomimetic surface matching
• Consistent quality across complex aerospace components
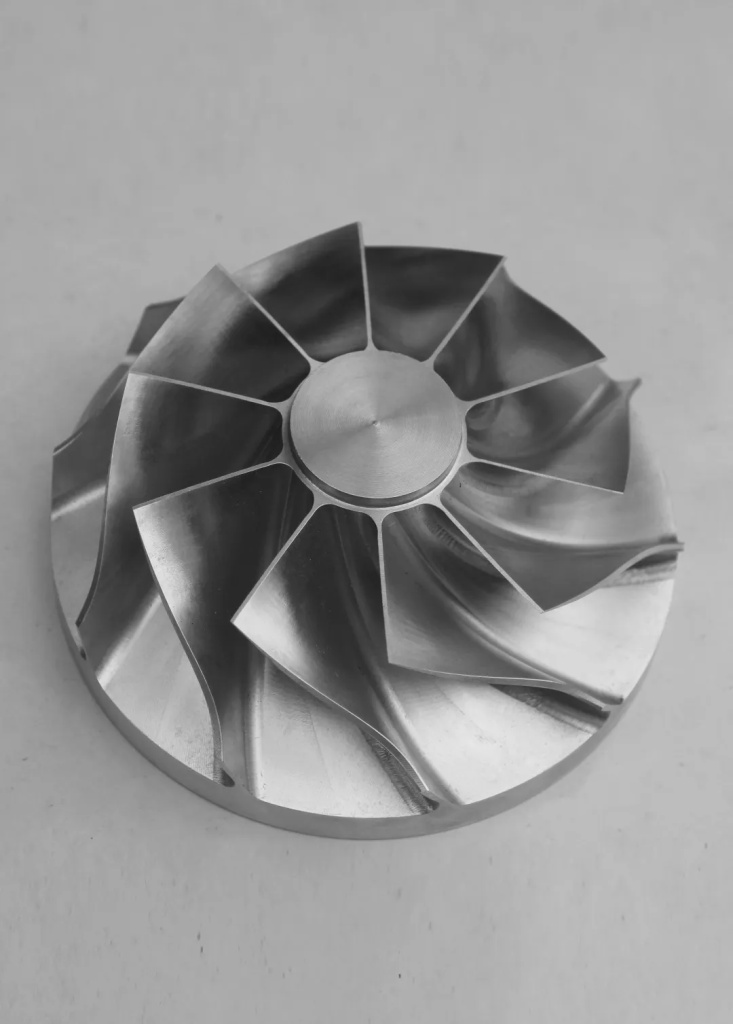


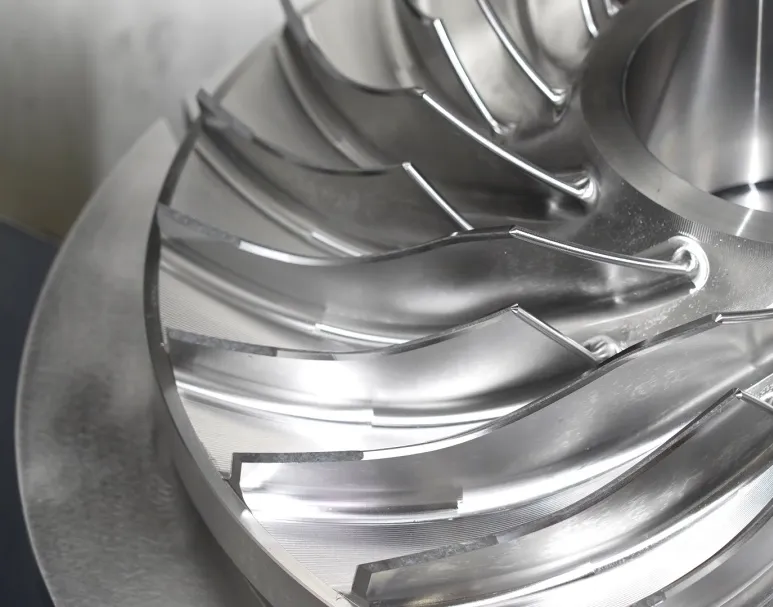
2. Enhanced Efficiency and Cost Reduction
5-axis machining efficiency extends beyond simple speed improvements. The technology delivers systematic process optimization through multiple mechanisms:
Time savings:
Single clamping eliminates setup, calibration, and re-clamping time required in 3-axis machining. Processing efficiency increases by over 30% compared to traditional methods. For example, automotive gearbox housing machining time drops from 4 hours to 1.5 hours, primarily through elimination of three separate clamping operations.
Tool life optimization:
Dual rotary axes enable dynamic cutting angle adjustment in 5-axis milling, maintaining optimal contact between tool cutting edge and workpiece. This reduces cutting forces, minimizes tool wear, and extends tool life by 140%.
Programming efficiency:
Advanced 5-axis programming systems support automatic path optimization, eliminating idle travel and maximizing effective cutting time. This creates a comprehensive win-win scenario of increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.

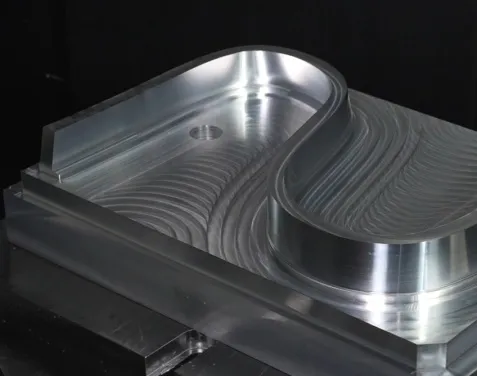
3. Complete Spatial Access: No-Dead-Angle Machining
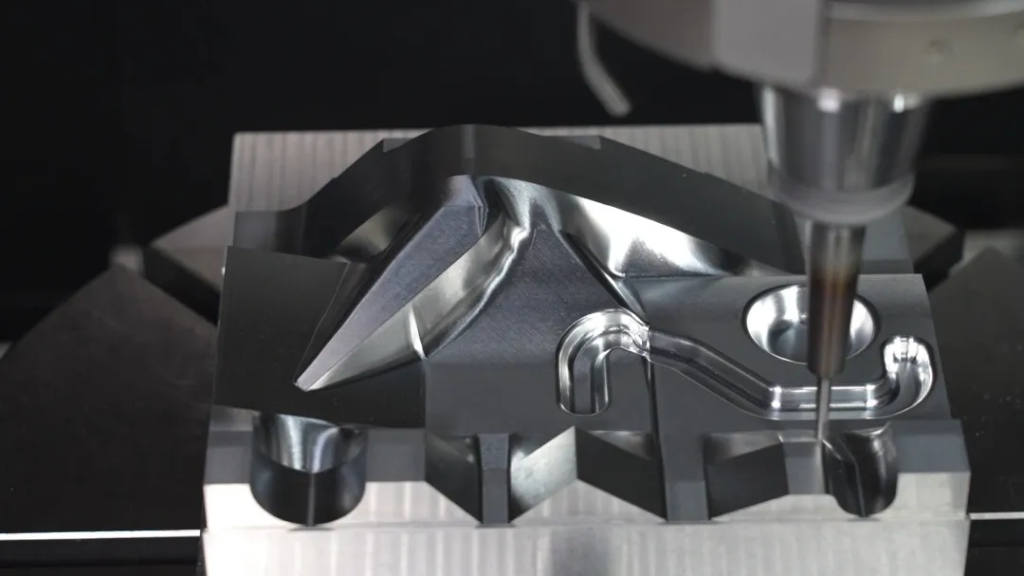
For complex geometries including deep cavities, beveled surfaces, and irregular holes, 5-axis CNC technology employs dual rotary axes combined with RTCP (Rotation Tool Center Point) linkage control.
Real-world application example:
In rocket nozzle deep cavity machining, traditional 3-axis tools face interference with cavity walls due to length limitations. 5-axis machines overcome this by:
• Adjusting workpiece tilt angle via A-axis
• Rotating workpiece via C-axis
• Utilizing RTCP real-time tool tip position compensation
• Enabling vertical tool penetration into cavity walls
• Achieving surface roughness below Ra0.8
• Eliminating subsequent polishing requirements
This “full-space coverage” capability stems from high-precision synchronous transmission of dual rotary axes. Torque motor direct drive systems achieve rotational accuracy of ±5 arcseconds, ensuring cutting stability under complex postures while freeing design from traditional machining constraints

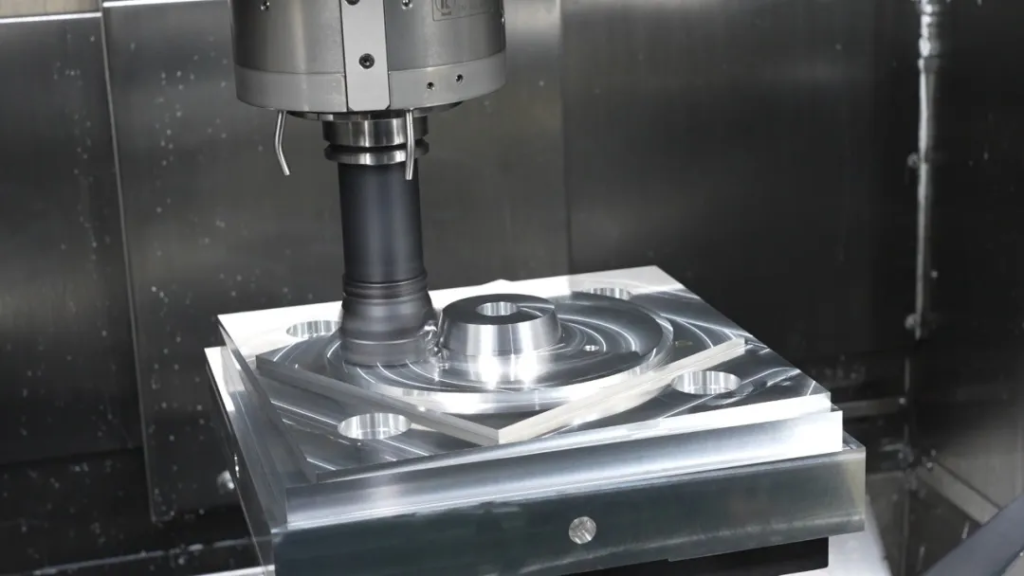
Future of 5-Axis Machining: Intelligence and Automation
The future of 5-axis CNC machining centers on intelligent manufacturing, with deep integration of AI, sensors, and data algorithms driving innovation. Key developments include:
AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance:
Advanced CNC systems now collect real-time machining parameters and build predictive models using AI algorithms. These systems accurately forecast tool wear and
machining errors, enabling preventative maintenance and fault warnings before failures occur.
Autonomous Optimization:
Modern 5-axis machining centers autonomously optimize cutting parameters and path planning, dynamically adapting to changing machining requirements without operator intervention.
Integration with Emerging Technologies:
The convergence of 5-axis machining with artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and
additive manufacturing will unlock unprecedented possibilities in precision manufacturing.
Conclusion: The Manufacturing Revolution Continues
The evolution from 3-axis machining’s “planar freedom” through 4-axis machining’s “rotational freedom” to 5-axis CNC machining’s “spatial freedom” represents more than technological advancement—it signifies a fundamental shift in manufacturing philosophy from “segmented assembly” to “integral forming.”Modern 5-axis machining technology no longer merely satisfies the basic requirement of “being able to machine.” Instead, it pursues higher-level objectives:
• Precision machining at micron levels
• Efficient machining with optimized processes
• Green machining for sustainable manufacturing
• Complex part production previously impossible
As 5-axis CNC systems continue integrating with AI, big data, and additive manufacturing, the technology will enable:
• Smarter machining decisions through AI analysis
• More efficient production processes
• Environmentally friendly manufacturing methods
• Unprecedented complex product design and manufacturing capabilities
This manufacturing revolution continues to accelerate. 5-axis machining stands at the forefront, writing an innovative chapter in modern manufacturing while propelling industrial civilization toward higher precision, greater efficiency, and enhanced sustainability.

